
Blockchain's Environmental Energy Challenges
As we stand at the intersection of technology and environmental responsibility, the impact of blockchain on our planet is more crucial than ever. With staggering electricity consumption and significant carbon emissions, understanding this dynamic is essential for responsible engagement in cryptocurrency.
What You Will Learn
- Blockchain technology currently consumes approximately 1% of the world’s electricity.
- Bitcoin mining emits around 100 million tons of CO2 annually, contributing to climate change.
- The shift from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) can reduce energy consumption by as much as 99.95%.
- The environmental impact of mining includes significant water usage and land disruption.
- Regulations are evolving to address the energy consumption and sustainability of blockchain practices.
Blockchain's Environmental Impact Comparison
An overview of energy consumption and carbon footprint across different blockchain technologies and consensus mechanisms.
Blockchain Annual Energy Use
300 TWh
(Estimated, comparable to entire countries)
Blockchain networks consume significant electricity, contributing to 1% of the world's total electricity. This usage raises alarms regarding environmental impact.
Bitcoin's Annual CO2 Emissions
100M Tons
(Projected CO2e, on par with small nations)
Bitcoin mining's Proof of Work (PoW) model results in a substantial carbon footprint, contributing significantly to global emissions.
Energy Reduction by Ethereum PoS
99.95%
(Estimated energy consumption decrease)
Ethereum's transition from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) dramatically reduces its energy consumption, showcasing a sustainable path.
Broader Environmental Impacts
- Water usage for cooling mining operations.
- Land disruption from mining infrastructure.
- Evolving regulations address sustainability.
The environmental concerns extend beyond direct energy use, encompassing critical resource management and regulatory responses.
The Environmental Impact of Blockchain Technology on Energy Consumption
The conversation around blockchain technology often centers on its energy consumption. Recent estimates suggest that blockchain networks consume a staggering amount of electricity, with projections indicating usage in the range of 300 TWh annually. To put this into perspective, that is comparable to the energy consumption of entire countries. The carbon emissions associated with this consumption, measured in CO2e, are raising alarms as we consider the environmental implications of such energy-intensive operations.
Understanding the true scale of energy consumption is essential as we navigate the complexities of blockchain technology. Awareness of these statistics can significantly influence how we view not only cryptocurrencies but also their broader impact on our planet. As someone passionate about educating others on cryptocurrency at How Does Bitcoin Work, I find it crucial to discuss these dynamics openly.
Understanding Blockchain Energy Consumption: Key Statistics and Data
- Blockchain technology is estimated to consume approximately 1% of the world’s electricity.
- Bitcoin mining alone is projected to emit around 100 million tons of CO2 each year.
- Research indicates that the energy use of Bitcoin has grown exponentially, contributing to the ongoing discussion about its sustainability.
These numbers highlight a reality we cannot ignore. The growing energy demands of blockchain technology pose significant challenges, sparking discussions on sustainability and environmental responsibility. It's a topic that needs our collective attention as we strive for a more informed approach to cryptocurrency.
Comparing Consensus Mechanisms: Energy Efficiency of PoW vs. PoS
One of the critical discussions in the realm of blockchain is the comparison between Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms. PoW, used by Bitcoin, requires extensive computational power for miners to validate transactions, leading to substantial energy consumption. In contrast, PoS significantly reduces energy requirements by allowing validators to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to "stake" as collateral.
The transition of Ethereum from PoW to PoS illustrates this shift. By adopting PoS, Ethereum aims to reduce its energy consumption by an estimated 99.95%, showcasing how consensus mechanisms can either exacerbate or mitigate environmental impacts. This evolution is not just a technical change; it represents a conscious effort to embrace sustainability within the blockchain space.
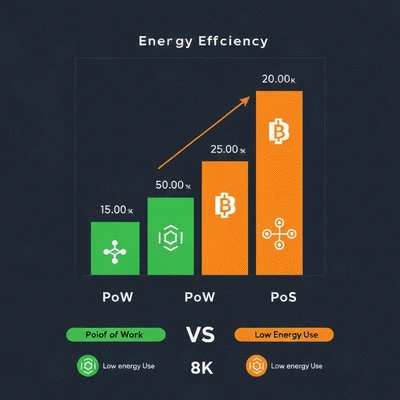
Exploring the Carbon Footprint of Major Cryptocurrencies
When analyzing the carbon emissions associated with cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin and Ethereum stand out as the most significant contributors. Bitcoin's mining operations result in a considerable carbon footprint due to its energy-intensive PoW model. Meanwhile, Ethereum’s transition to PoS is a step toward reducing its environmental impact.
- Bitcoin's annual emissions are on par with those of small nations.
- Ethereum's shift to PoS is poised to drastically lower its carbon emissions.
- Alternative cryptocurrencies are exploring eco-friendlier mining solutions and consensus mechanisms to reduce their footprints.
The implications of these carbon footprints extend beyond just numbers; they feed into the larger narrative of climate change and the role that cryptocurrency plays in it. As we delve deeper into the world of cryptocurrency, understanding these aspects is vital for informed decision-making and responsible investment.
Pro Tip
Did you know? Transitioning to more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS) not only reduces carbon emissions significantly but also promotes a more sustainable blockchain ecosystem. As Ethereum's shift to PoS aims to cut its energy consumption by an estimated 99.95%, this sets a powerful precedent for other cryptocurrencies to follow suit.
Summarizing the Environmental Impact of Blockchain and Sustainable Solutions
Throughout our exploration of blockchain technology, we've uncovered several key points about its environmental impact and the viable sustainable solutions available. From understanding the energy consumption involved in various consensus mechanisms to evaluating the carbon footprint of popular cryptocurrencies, it’s clear that the intersection of blockchain and sustainability is critical for future development.
We’ve discussed the energy challenges posed by Proof of Work (PoW) versus Proof of Stake (PoS) and the need for more efficient practices in the industry. Additionally, the environmental implications regarding water usage and land use from mining operations have shown us that blockchain isn't just a tech issue; it’s also an environmental concern. As we navigate these challenges, it's crucial to consider the regulatory landscape shaping blockchain practices.
- Blockchain energy consumption is substantial, with estimates in the terawatt-hour (TWh) range.
- Consensus mechanisms like PoW are less energy-efficient than PoS, especially as Ethereum transitions.
- Major cryptocurrencies contribute significantly to carbon emissions, impacting climate change.
- Water usage and land disruption from mining operations are ongoing environmental concerns.
- Regulations are evolving to address blockchain's energy consumption and sustainability.
In summary, while blockchain holds incredible potential, we must also acknowledge and tackle its environmental impact. Engaging in sustainable practices can help mitigate these effects, paving the way for a greener future in cryptocurrency and blockchain technology.
Frequently Asked Questions About Blockchain's Environmental Impact
- Q: How much electricity does blockchain technology consume globally?
- A: Blockchain technology is estimated to consume approximately 1% of the world’s electricity, with annual usage projections around 300 TWh. This is comparable to the energy consumption of entire countries.
- Q: What is Bitcoin's annual carbon footprint?
- A: Bitcoin mining is projected to emit around 100 million tons of CO2 annually, contributing significantly to global emissions, on par with small nations.
- Q: How does Proof of Stake (PoS) compare to Proof of Work (PoW) in terms of energy efficiency?
- A: Proof of Stake (PoS) is significantly more energy-efficient than Proof of Work (PoW). For instance, Ethereum's transition to PoS is expected to reduce its energy consumption by an estimated 99.95%.
- Q: Are there other environmental concerns related to blockchain beyond energy consumption?
- A: Yes, beyond energy consumption, blockchain operations, particularly mining, also raise concerns about water usage for cooling and potential land disruption from infrastructure development.
- Q: What measures can be taken to promote sustainable blockchain practices?
- A: Promoting sustainable blockchain practices involves researching and implementing renewable energy sources for mining, supporting projects focused on carbon offsetting and energy efficiency, staying informed about regulatory changes, and engaging with communities dedicated to sustainable practices.
Call to Action: Engaging Stakeholders in Sustainable Blockchain Practices
As we wrap up this discussion, I encourage you to consider your role in promoting sustainable blockchain practices. Whether you're a miner, developer, or investor, every action counts! By advocating for and adopting cleaner practices, we can collectively work toward a more sustainable blockchain ecosystem.
Here are some steps you can take to engage with this important issue:
- Research and implement renewable energy sources for mining operations.
- Support projects that focus on carbon offsetting and energy efficiency.
- Stay informed about regulatory changes that impact blockchain energy use.
- Engage with communities and forums focused on sustainable practices.
For further resources, visit How Does Bitcoin Work, where we provide guides and tutorials to help you understand the complexities of blockchain and its environmental impact. Let's work together to create a sustainable future for blockchain technology!
Recap of Key Points
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
- Blockchain technology is responsible for approximately 1% of the world’s electricity consumption.
- Bitcoin mining emits around 100 million tons of CO2 annually, comparable to the emissions of small nations.
- The transition from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) can drastically reduce energy consumption, as seen with Ethereum's shift aiming for a 99.95% reduction.
- Understanding the environmental implications of blockchain, including water usage and land disruption, is crucial for sustainable development.
- Engaging in sustainable practices and staying informed about regulatory changes can help mitigate the environmental impact of blockchain technology.





Bitcoin Wallets in DeFi and NFTs
Secure Your Bitcoin Investments Today
Bitcoin Mining's Role in Security
Recovering Your Lost Bitcoin Keys
The Importance of Bitcoin Today